DMOS vs VMOS vs LDMOS | Difference between DMOS, VMOS, LDMOS
This page compares DMOS vs VMOS vs LDMOS and mentions difference between DMOS, VMOS and LDMOS.It mentions DMOS structure, VMOS structure and LDMOS structure.
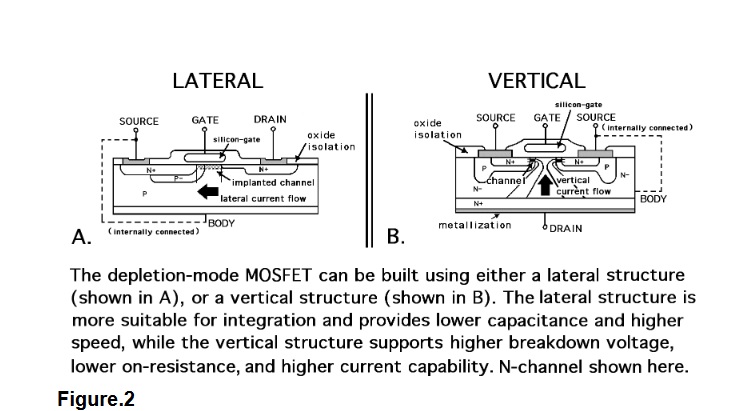
DMOS basics | DMOS structure
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET), also known as the metal–oxide–silicon transistor (MOS transistor, or MOS), is a type of insulated-gate field-effect transistor that is fabricated by the controlled oxidation of a semiconductor, typically silicon. The DN2470 is a low threshold depletion-mode (normally-on) transistor utilizing an advanced vertical DMOS structure and well-proven silicon-gate manufacturing process. Vertical DMOS FET Absolute Maximum Ratings Parameter Value Drain-to-source voltage BV DSS Drain-to-gate voltage BV DGS Gate-to-source voltage ±20V Operating and storage temperature -55OC to +150OC Absolute Maximum Ratings are those values beyond which damage to the device may occur. Functional operation under these conditions is not implied.
DMOS stands for Double-Diffused MOS.The device is widely used in switching applications requiring high voltage and high frequency behavior.The other applications of DMOS are Inkjet printheads, automobile control electronics, power supplies etc.
Dmos Power Mosfet
The figure-1 depicts DMOS structure. Following are the properties of DMOS device.
• The DMOS device uses a double diffusion process.
• The p-region and the n+ source regions are diffused through commonwindow. This is defined by edge of the gate.
• The p-region is being diffused deeper compare to n+ source.
• The surface channel length is defined as the lateral diffusion distancebetween the p-substrate and the n+ source.
• The breakdown voltage and on-resistance are two important parameters of DMOS device.
• Due to high voltage and high frequency characteristics it is similar to BJT.
• The very high breakdown voltage is achieved due to lightly doped drift region between Drain and channel regions.
• The n-drift region thickness should be as thin as possible in order to achieve lower drain resistance.
VMOS basics | VMOS structure
VMOS stands for Vertical Metal Oxide Silicon.The device has V-shaped gate region.The devices are used for applications requiring medium powers such aspower amplifiers and switching.
The figure-2 depicts VMOS structure. Following are the properties of VMOS device.
• It consists of shaped groove.
• Due to source at top and drain at bottom, the current flows vertically rather than horizontally.
• V shaped gate makes cross-sectional area of source to drain path larger.Hence lower ON resistance of the device can be achieved which allows much higher power.
• The gate consists of metallised area over the V groove which controls current flow in P-region.
• VMOS structure is more complex compare to traditional FET device.This makes it more expensive.
LDMOS basics | LDMOS structure
Dmos Mosfet Testing

LDMOS is asymmetric power MOSFET device.It is designed for applications requiring lower on-resistance and higher blocking voltage.
In LDMOS channel current is being controlled by vertical electric field (E).This E-field is induced by gate and lateral field which exists between S (Source) and D (Drain).In LDMOS device, channel is determined by three parameters viz. gate length, drain diffusion and source diffusion.
Wps writer software download. The device is fabricated using diffusion and ion implantation processes.Initially p-type region is constructed.Later shallow p+ and n+ regions are being formed.The source and drain contact regions are created from n+ regions.The p+-region contacts with the p-type body. This is shorted to source part.This will eliminate body effect.The figure-3 depicts LDMOS structure.
Refer Advantages and disadvantages of LDMOS>> for more information.
MOSFET and BJT related links
MOSFET vs IGBT➤
PNP Transistor Vs NPN Transistor➤
BJT vs FET➤
JUGFET vs MOSFET➤
Depletion MOSFET vs Enhancement MOSFET➤
MOSFET Fabrication Technology➤
MOSFET vs BJT-Difference between MOSFET and BJT➤
Application Note-MOSFET as switch and amplifier➤
Difference between NMOS vs PMOS➤
What is Difference between
difference between FDM and OFDM
Difference between SC-FDMA and OFDM
Difference between SISO and MIMO
Difference between TDD and FDD
Difference between 802.11 standards viz.11-a,11-b,11-g and 11-n
OFDM vs OFDMA
CDMA vs GSM
RF and Wireless Terminologies
Share this page
Dmos Vs Mosfet
Translate this page

